Inheritance:
Not just in Java, but in General Inheritance in Object Oriented Programming has lot of advantages…
Advantages:-
- One of the key benefits of inheritance is to minimize the amount of duplicate code in an application by sharing common code amongst several subclasses. Where equivalent code exists in two related classes, the hierarchy can usually be refactored to move the common code up to a mutual superclass. This also tends to result in a better organization of code and smaller, simpler compilation units.
- Inheritance can also make application code more flexible to change because classes that inherit from a common superclass can be used interchangeably. If the return type of a method is superclass
- Reusability - facility to use public methods of base class without rewriting the same.
- Extensibility - extending the base class logic as per business logic of the derived class.
- Data hiding - base class can decide to keep some data private so that it cannot be altered by the derived class
- Overriding -With inheritance, we will be able to override the methods of the base class so that meaningful implementation of the base class method can be designed in the derived class.
Disadvantages:-
- One of the main disadvantages of inheritance in Java (the same in other object-oriented languages) is the increased time/effort it takes the program to jump through all the levels of overloaded classes. If a given class has ten levels of abstraction above it, then it will essentially take ten jumps to run through a function defined in each of those classes
- Main disadvantage of using inheritance is that the two classes (base and inherited class) get tightly coupled. This means one cannot be used independent of each other. Also, change in base class can effect derived class.
- Also with time, during maintenance adding new features both base as well as derived classes are required to be changed. If a method signature is changed then we will be affected in both cases (inheritance & composition)
- If a method is deleted in the "base class" or aggregate, then we will have to re-factor in case of using that method.Here things can get a bit complicated in case of inheritance because our programs will still compile, but the methods of the subclass will no longer be overriding base class methods. These methods will become independent methods in their own right.
Association, Composition and Aggregation in Java
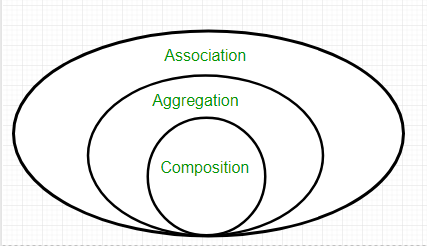
Association
Association is relation between two separate classes which establishes through their Objects. Association can be one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, many-to-many.
In Object-Oriented programming, an Object communicates to other Object to use functionality and services provided by that object. Composition and Aggregation are the two forms of association.
In Object-oriented programming, one object is related to other to use functionality and service provided by that object. This relationship between two objects is known as the association in object oriented general software design and depicted by an arrow in Unified Modelling language or UML. Both Composition and Aggregation are the form of association between two objects, but there is a subtle difference between composition and aggregation, which is also reflected by their UML notation. We refer association between two objects as Composition, when one class owns other class and other class can not meaningfully exist, when it's owner destroyed, for example, Human class is a composition of several body parts including Hand, Leg and Heart. When human object dies, all it's body part ceased to exist meaningfully, this is one example of Composition.In Object-Oriented programming, an Object communicates to other Object to use functionality and services provided by that object. Composition and Aggregation are the two forms of association.
Programmers often confuse between Association, Composition and Aggregation in Object oriented design discussions, this confusion also makes the difference between Association, Composition and Aggregation one of the popular questions in Java Interviews, only after the difference between abstract class and interface .
Another example of Composition is Car and it's part e.g. engines, wheels etc. Individual parts of the car can not function when a car is destroyed. While in the case of Aggregation, including object can exists without being part of the main object e.g. a Player which is part of a Team, can exist without a team and can become part of other teams as well.
Another example of Aggregation is Student in School class, when School closed, Student still exist and then can join another School or so. In UML notation, a composition is denoted by a filled diamond, while aggregation is denoted by an empty diamond, which shows their obvious difference in terms of strength of the relationship.
The composition is stronger than Aggregation. In Short, a relationship between two objects is referred as an association, and an association is known as composition when one object owns other while an association is known as aggregation when one object uses another object.
In this OOPS tutorial, we will see a couple of more examples to understand difference between Association, Composition and Aggregation better.
An Example of Association, Composition and Aggregation in Java
Here is an example of composition and aggregation, in terms of Java Code. By looking at this code, you can gauge differences between these two. By the way, Composition is also very much preferred in object oriented design over inheritance, even Joshua Bloch has stated its importance in the classic book, Effective Java.Composition : Since Engine is-part-of Car, the relationship between them is Composition. Here is how they are implemented between Java classes.
public class Car {
//final will make sure engine is initialized private final Engine engine; public Car(){ engine = new Engine(); } } class Engine { private String type; }
Aggregation : Since Organization has Person as employees, the relationship between them is Aggregation. Here is how they look like in terms of Java classes
public class Organization {
private List employees;
}
public class Person {
private String name;
}
UML Diagram of Association, Composition and Aggregation
UML has different notations to denote aggregation, composition and association. Association is denoted by the simple arrow while aggregation is denoted by empty diamond-head arrow and composition is denoted by filled diamond-head arrow. When you draw UML diagram for two related class A and B, where A is associated with B then its denoted by A -> B. Similar way is used to show aggregation and composition between two classes. Here are UML notations for different kind of dependency between two classes.As I said all three denotes relationship between object and only differ in their strength, you can also view them as below, where composition represents strongest form of relationship and association being the most general form.
Association vs Composition vs Aggregation
Here is the list of differences between Composition and Aggregation in point format, for quick review. As I said the key difference between them comes from the point that in the case of Composition, One object is OWNER of another object, while in the case of aggregation, one object is just a USER or another object.1) If A and B two classes are related to each other such that, B ceased to exist, when A is destroyed, then the association between two objects is known as Composition. An example is Car and Engine. While if A and B are associated with each other, such that B can exist without being associated with A, then this association in known as Aggregation.
See Head First Object-Oriented Analysis and Design for more examples of Composition and Association in OOP.
2) In the case of Composition A owns B e.g. Person is the owner of his Hand, Mind and Heart, while in the case of Aggregation, A uses B e.g. Organization uses People as an employee.
3) In UML diagram Association is denoted by a normal arrow head, while Composition is represented by filled diamond arrow head, and Aggregation is represented by an empty diamond arrow head, As shown in below and attached diagram in the third paragraph.
Association A---->B
Composition A-----<filled>B
Aggregation A-----<>B
4) Aggregation is a lighter form of Composition, where a sub-part object can meaningfully exist without main objects.
5) In Java, you can use final keyword to represent Composition. Since in Composition, Owner object expects a part object to be available and functions, by making it final, your provide guarantee that, when Owner will be created, this part object will exist. This is actually a Java idiom to represent a strong form of association i.e. composition between two objects.
6) Another interesting word, which comes handy to understand difference between Composition and Aggregation in software design is "part-of" and "has". If one object is-part-of another object e.g. Engine is part of Car, then association or relationship between them is Composition. On the other hand, if one object just has another object e.g. Car has the driver then it's Aggregation.
That's all on the difference between Association, Composition and Aggregation in UML, Java and Object oriented design. Since object oriented analysis is more about defining the relationship between object, it's important to know what kind of relationship exists between them, composition and aggregation is a two way of representing relationship between two objects.
Read more: https://javarevisited.blogspot.com/2014/02/ifference-between-association-vs-composition-vs-aggregation.html#ixzz637jA2EDe




No comments:
Post a Comment